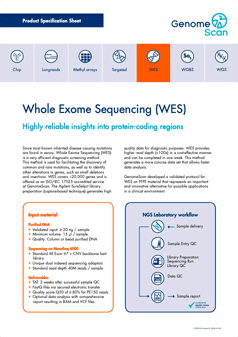
WES is a highly reliable tool for identifying variants. Especially for the analysis of clinical samples, WES provides a cost-effective alternative to whole genome sequencing (WGS).

Whole Exome Sequencing

Why sequence whole exomes?

Main advantages of WES
Exons make up 1 to 2% of the entire human genome, and harbor the majority of mutations that are associated with inherited diseases.
Diagnostic processes that utilize sequencing focused on these regions can provide results more effectively.
- Full coverage of protein-coding regions
- Strong reliability enabled by high sequencing depth
- Generates small set of data for easy functional interpretation
- Fast results
- Low costs for sequencing, data storage and analysis
- Broad insights when a phenotype does not show association to a known mutation
Trio sequencing
As a diagnostic strategy for Mendelian disorders, family-based WES can accelerate interpretation of results and disease. With trio sequencing, both the patient and their parents’ exomes are analyzed, the comparison resulting in the identification of de-novo mutations.
Data analysis
GenomeScan’s bioinformatics experts apply optimized pipelines for preprocessing (trimming and alignment to reference genome), as well as analyzing (variant calling and disease annotations) your dataset. With our customizable workflows, we help you receive reliable and publication ready results.
We have summarized key information about our whole exome sequencing service into a service specification sheet.

In this TechNote, you can find information on procedure validation methods and results for our whole exome sequencing service.
Let's get the conversation started for your next NGS project
Please either fill in this form or email us directly at info@genomescan.nl
and we will get in touch with you to discuss your requirements





